如何为 Flask Web 应用配置 Nginx
简介
在本文中,我将介绍什么是 Nginx 以及如何为 Flask Web 应用配置 Nginx。本文是《部署 Flask 应用》系列文章的一部分。我曾找到过多份关于 Nginx 及其配置的文章,但我希望能更深入其细节,了解如何使用 Nginx 为 Flask Web 应用服务以及如何为此进行配置。Nginx 的配置文件有点让人困惑,因为大多数的文档仅仅是简单罗列了一个配置文件,而没有对配置中每一步做了什么进行任何解释。希望本文能让你清晰地理解如何为你的应用配置 Nginx。
什么是 Nginx?
在 Nginx(发音为“engine-X”)的官网中,有着这个工具的概要描述:
Nginx 是一款免费、开源、高性能的 HTTP 服务器以及反向代理,同时也可以作为 IMAP/POP3 代理服务器。Nginx 以其高性能、稳定性、丰富的功能、简单的配置、低资源消耗而闻名。
我们可以拓展理解此说明…… Nginx 是一个可以为你的 Web 应用处理 HTTP 请求的服务器。对于典型的 Web 应用,Nginx 可以配置为 HTTP 请求进行以下操作:
- 将请求 反向代理 至上游服务器(例如 Gunicorn、uWsgi、Apache 等)。
- 为静态资源(Javascript 文件、CSS 文件、图像、文档、静态 HTML 文件)提供服务。
同时 Nginx 也提供了负载均衡功能,可以让多个上游服务器为请求提供服务,不过在本文中暂不讨论此功能。
下图为描述 Nginx 如何为 Flask Web 应用提供服务的简图:
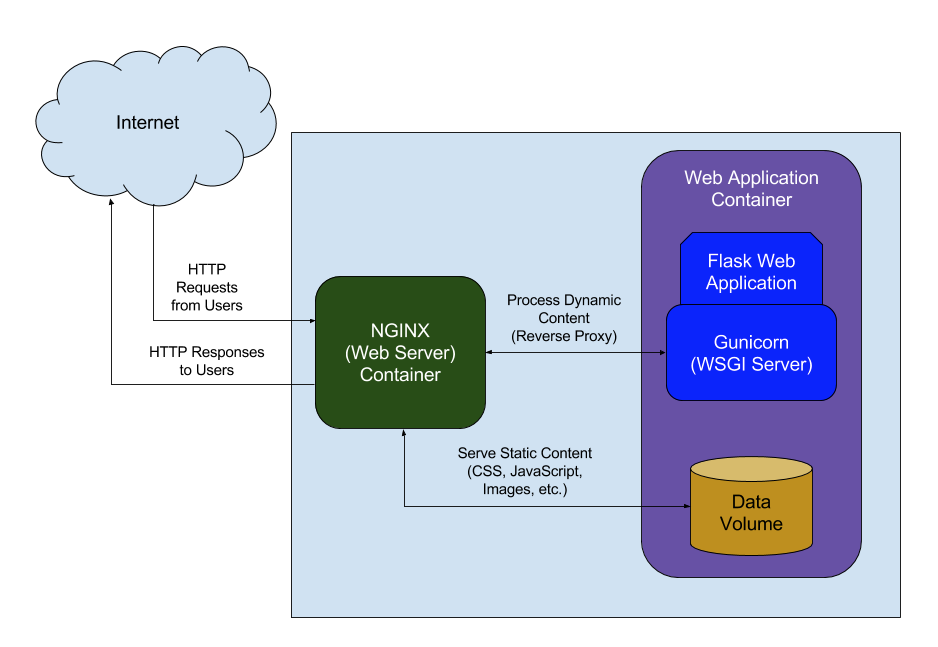
Nginx 会处理来自因特网(比如来自你应用的用户)的 Http 请求。根据你对 Nginx 的配置,它可以直接提供并向请求源返回静态内容(Javascript 文件、CSS 文件、图像、文档、静态 HTML 文件)。此外,它也能将请求反向代理至 WSGI(Web Server Gateway Interface)以让你在 Flask Web 应用中生成动态内容(HTML)并返回给用户。
上面的示意图假定用户使用了 Docker,但不使用 Docker 时 Nginx 的配置也与此十分相似(仅仅省略了图中容器的概念)。
为什么你需要 Nginx 与 Gunicorn?
Nginx 作为一个 HTTP 服务器,在许多应用中都被使用:列表。它提供了许多的功能,但无法直接为 Flask 应用提供服务。而 Gunicorn 可以做到这一点。Nginx 收到 HTTP 请求,并将其传递给 Gunicorn 交由你的 Flask 应用进行处理(比如你在 view.py 中定义的路由)。Gunicorn 是一个 WSGI 服务器,可以处理 HTTP 请求,并将它们通过路由交给任何支持 WSGI 的 python 应用处理(比如 Flask、Django、Pyramid 等)。
Nginx 配置文件的结构
注意:本文应用的是 Nginx v1.11.3,配置文件所在的位置根据你 Nginx 版本的不同会有所变化,比如 /opt/nginx/conf/。
根据你安装、使用 Nginx 方式的不同,配置文件的结构会略有不同。大多数的配置结构如下所示:
结构 1
如果你使用的是从源代码编译得到的 Nginx 或者官方的 Docker 镜像,那么配置文件在 /etc/nginx/ 中,主配置文件为 /etc/nginx/nginx.conf。在 /etc/nginx/nginx.conf 的最下面的一行会将位于 /etc/nginx/conf.d/ 目录下的其余配置文件内容载入配置中:
- include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
结构 2
如果你是通过包管理器(比如 Ubuntu 的 apt-get)安装的 Nginx,那么你的 /etc/nginx/ 下会有下面两个子目录:
- sites-available – 包含为多个网站准备的多个配置文件。
- sites-enabled – 包含一个指向 sites-available 目录中配置文件的软链接。
这两个目录继承于 Apache,将应用于 Nginx 的配置。
由于我的 Flask 应用使用的是 Docker 部署,因此在本文将主要关注上面的结构 1。
Nginx 的配置
Nginx 的顶层配置文件是 nginx.conf。Nginx 接受多层级的配置文件,这也使得用户可以针对自己的应用进行弹性的配置。如需了解配置文件中各参数的详细信息,可以参阅 Nginx 官方文档。
在 Nginx 中,由配置块(block)来组织各个配置参数。以下为在本文中我们将提到的配置块:
- Main – 定义于 nginx.conf(所有不属于配置块的参数均属 Main 块)
- Events – 定义于 nginx.conf
- Http – 定义于 nginx.conf
- Server – 定义于 application_name.conf
将这些配置块拆分至不同的文件,可以让你在 nginx.conf 中定义 Nginx 的高级别配置,在其它的 *.conf 文件中为你的应用定义虚拟主机或服务器的参数。
nginx.conf 详细说明
安装 Nginx 时自带的默认 nginx.conf 文件可以适用于大多数服务器的初步配置。让我们仔细探查 nginx.conf 的内容,并思考如何拓展这里的默认设置。
Main 部分
nginx.conf 的 main 配置块(即那些不在配置块中的参数)为:
1 | user nginx; |
第一个参数(user)将定义 Nginx 服务器的拥有者以及运行用户。当 Nginx 通过 Docker 容器运行时,使用默认值就够了。
第二个参数(worker_processes)定义了 worker processes(工作进程)的数量。此参数推荐的默认值为当前服务器使用内核的数量。对于基础的虚拟私有服务器(VPS)来说,默认值 1 就是个不错的选择。当你拓展 VPS 性能时可以增加这个数字。
第三个参数(error_log)定义了错误日志在文件系统中存放的位置,并能额外定义一个参数来规定需要记录日志的最小错误等级。这个参数使用默认值即可。
第四个参数(pid)定义了用于存储 Nginx 主进程 pid 的文件位置。这个参数使用默认值即可。
events 配置块
events 配置块定义了一些会影响连接处理的参数。它也是 Nginx.conf 文件中第一个配置块:
1 | events { |
在这个配置块中仅有一个单独的参数(worker_connections),定义了工作进程可以打开的最大并发连接数。默认值定义了总共可用 1024 个连接,无需更改(但你需要计算用户请求站点及请求 WSGI 服务器的连接数)。
http 配置块
http 配置块定义了一些关于 Nginx 如何处理 HTTP Web 流量的参数。它是 nginx.conf 文件中第二个配置块:
1 | http { |
第一个参数(include)指定了需要引入的配置文件,在此引入的是位于 /etc/nginx/ 的 mime.types 文件,这个文件定义了各种 Nginx 支持的文件类型。此参数应该保持默认值。
第二个参数(default_type)指定了默认给用户返回的文件类型。对于
Flask 应用来说,返回的是动态生成的 HTML 文件,因此这个参数应改为
default_type text/html;
第三个参数(log_format)指定了日志的格式,应当保持默认值。
第四个参数(access_log)指定了 Nginx 日志的访问位置,应当保持默认值。
第五个参数(send_file)以及第六个参数(tcp_nopush)稍微有点复杂。可以参阅《优化 Nginx》一文来了解这些参数(包括 tcp_nodelay)的详细情况。由于我们打算用 Nginx 来传递静态内容,因此可以这么设置这些参数:
1 | sendfile on; |
第七个参数(keepalive_timeout)定义了与客户端保持连接的超时时长,应当保持默认值。
第八个参数(gzip)定义了 gzip 压缩算法的使用方法,以减少传输数据量。虽然数据量减少了,但也因此增加平台在压缩过程中的性能消耗,好处两两抵消,因此保持它的默认值(off)。
第九个,也是最后一个参数(include)定义了位于 /etc/nginx/conf.d/ 下后缀名为 .conf 的其它配置文件。现在我们将使用这些配置文件定义静态内容服务器以及 WSGI 服务器的反向代理。
nginx.conf 的最终配置
在 nginx.conf 默认设置之上,我们需要根据需要调整一些参数(并加上注释),下面为最终版本的 nginx.conf:
1 | # Define the user that will own and run the Nginx server |
为静态内容部署及反向代理配置 Nginx
如果你查看默认的 /etc/nginx/conf.g/default.conf,可以看到它提供了一个简单的服务器配置块,并给了许多取消注释即可使用的可选配置。我们不会挨个去研究这个文件中的配置,而是直接探讨对于我们部署静态内容以及 WSGI 反向代理有用的关键参数。以下是推荐的 application_name.conf 配置:
1 | # Define the parameters for a specific virtual host/server |
服务器配置块为特定的虚拟主机或服务器定义了参数。通常为你在 VPS 上部署的单个 Web 应用。
第一个参数(root)定义了被请求的内容所存储的位置。当 Nginx 收到用户请求时,它便会在此目录中查找。由于在默认的”/“路径中定义过了,因此可以注释掉这个不必要的参数。
第二个参数(index)定义了在请求未指定页面时(比如访问 www.kennedyfamilyrecipes.com)所得到的默认页面。由于我们使用的是 Flask Web 应用生成的动态内容,因此需要注释掉这个参数。
前两个参数(root 和 index)都包含在此配置文件中,在一些情况下可以用于 Nginx 的配置。
第三个参数(server_name)和第四个参数(listen)需要一同使用。如果你的 Web 应用程序已经部署好了,那么你需要设置这些参数为:(注,端口默认为 80,此时不需要填)
1 | server { |
如果你除了 www.kennedyfamilyrecipes.com 之外还要部署另一个 Flask 应用 blog.kennedyfamilyrecipes.com,那么你需要将”server“配置块拆开,分别配置”user_name“和”listen“:
1 | server { |
Nginx 将选择最匹配请求的”server_name“。也就是说对”blog.kennedyfamilyrecipes.com“的请求会优先匹配”blog.kennedyfamilyrecipes.com“而不是”*.kennedyfamilyrecipes.com“。
第五个参数(charset)定义了响应头”Content-Type“的字符集值,应当设置为”utf-8“。
第一个”location“配置块定义了 Nginx 需要递送位于以下位置的静态内容:
1 | location /static { |
location 配置块定义了如何处理请求的 URI(域名或 IP、端口号之后的部分)。在这第一个 location 配置块(/static)中,我们定义了 Nginx 将会处理来自 www.kennedyfamilyrecipes.com/static/ 的请求,检索位于 /usr/src/app/project/static 目录下的文件。例如,请求 www.kennedyfamilyrecipes.com/static/img/img_1203.jpg 将会返回位于 /usr/src/app/project/static/img/img_1203.jpg 的图片文件。如果文件不存在,则向用户返回 404 错误码(NOT FOUND)。
第二个 location 配置块("/")定义反向代理。这个 location 配置块会定义 Nginx 如何将请求传递给 我们的 Flask 应用接口所在的 WSGI(Gunicorn)服务器。仔细看看其中的每个参数:
1 | location / { |
第一个参数(proxy_pass)定义了接收转发请求的代理服务器的位置。如果你想将请求转发至本机的服务器时可以使用:
1 | proxy_pass http://localhost:8000/; |
如果你希望将请求转发给指定的 Unix socket 时(比如和 Nginx 运行在同一台机器中的 Gunicorn 服务器),可以使用:
1 | proxy_pass http://unix:/tmp/backend.socket:/ |
如果你使用 Docker 容器运行的 Nginx,希望与容器中的 Gunicorn 进行通信,那么可以直接使用运行 Gunicorn 的容器名称:
1 | proxy_pass http://web:8000; |
第二个参数(proxy_pass_header)可以让你重新定义发往上游服务器(比如 Gunicorn)的请求的头部。这个参数可以进行以下四次设置:
- Nginx 服务器的名称及端口(Host $host)
- 原始客户端请求的模式(比如是 http 请求还是 https 请求)(X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme)
- 用户的 IP 地址(X-Real-IP $remote_addr)
- 至当前节点位置,客户端经过的所有代理的 IP 地址(X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for)
第三个参数(client_max_body_size)定义了文件上传允许的最大大小,对于需要上传文件的 Web 应用来说非常重要。由于图像大小一般在 2 MB 内,因此在这儿设置 5 MB 基本上可以满足任何图像。
总结
本文介绍了什么是 Nginx 服务器,以及如何为一个 Flask 应用对其进行配置。Nginx 是大多数 Web 应用的关键组件,它为用户提供静态内容、反向代理请求至上游服务器(在我们的 Flask Web 应用中是 WSGI),以及负载均衡(本文未提及)。希望看完本文后你能更轻松地理解 Nginx 的配置!
引用资料
How to Configure NGINX (Linode)
NGINX Pitfalls and Common Mistakes
How to Configure the NGINX Web Server on a VPS (DigitalOcean)
Understanding NGINX Server and Location Block Selection Algorithms (DigitalOcean)
NGINX Optimization: Understanding sendfile, tcp_nodelay, and tcp_nopush
本文发布于掘金 https://juejin.im/post/5a795febf265da4e94499949